
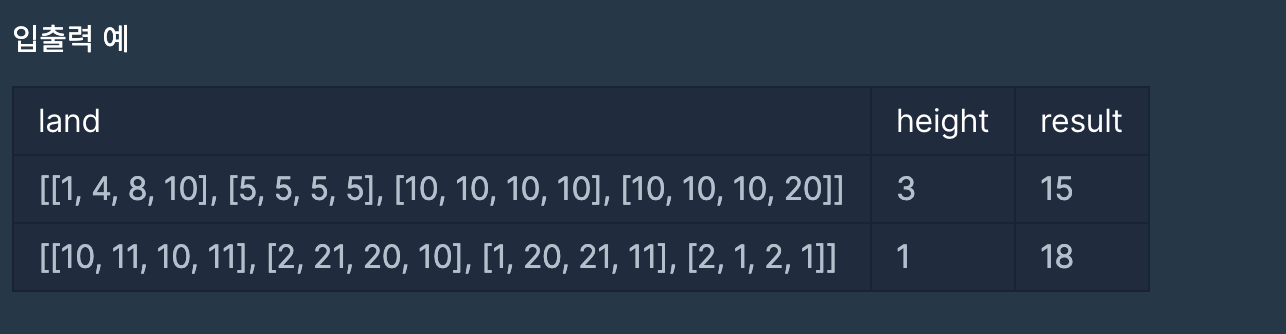
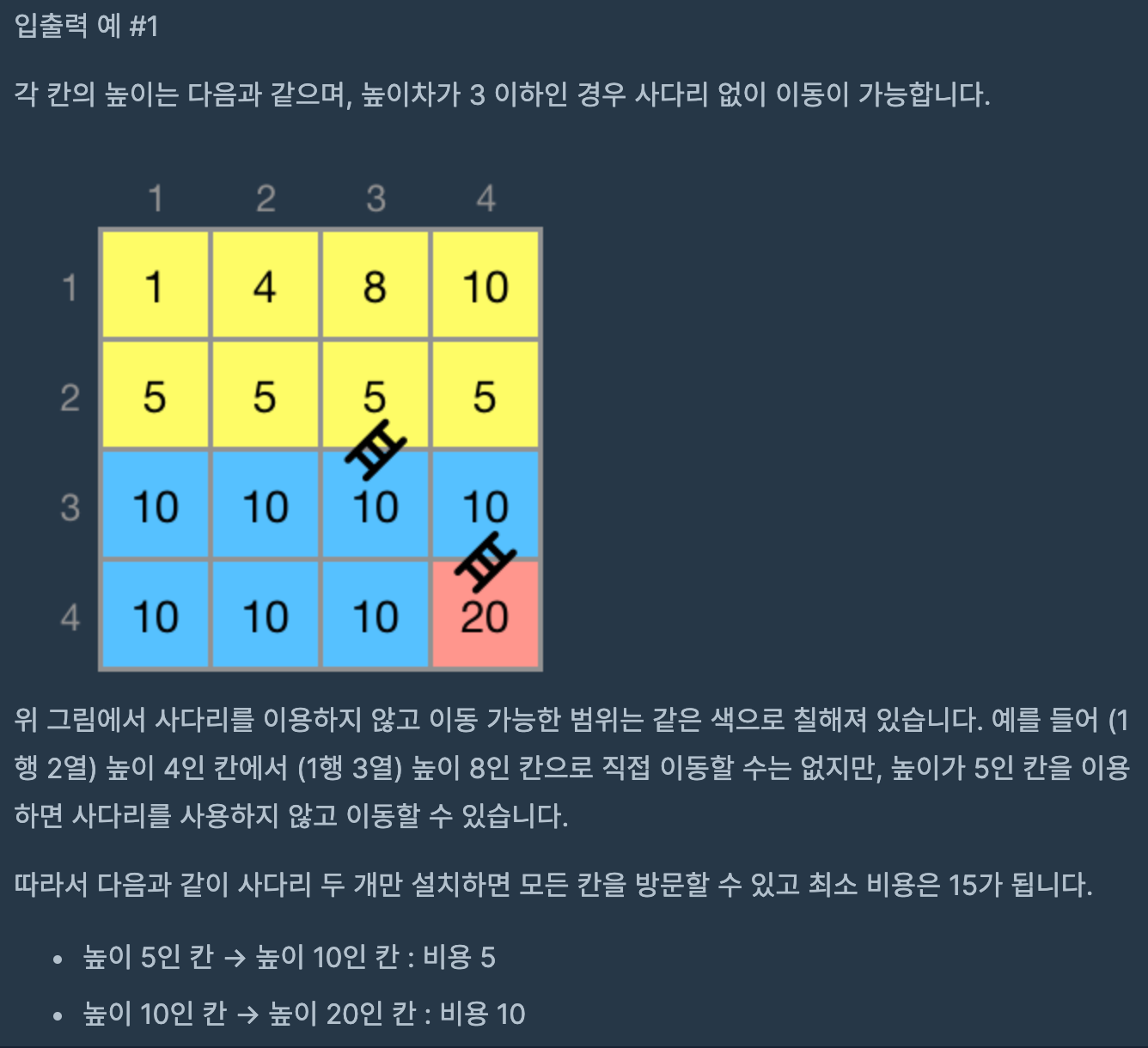
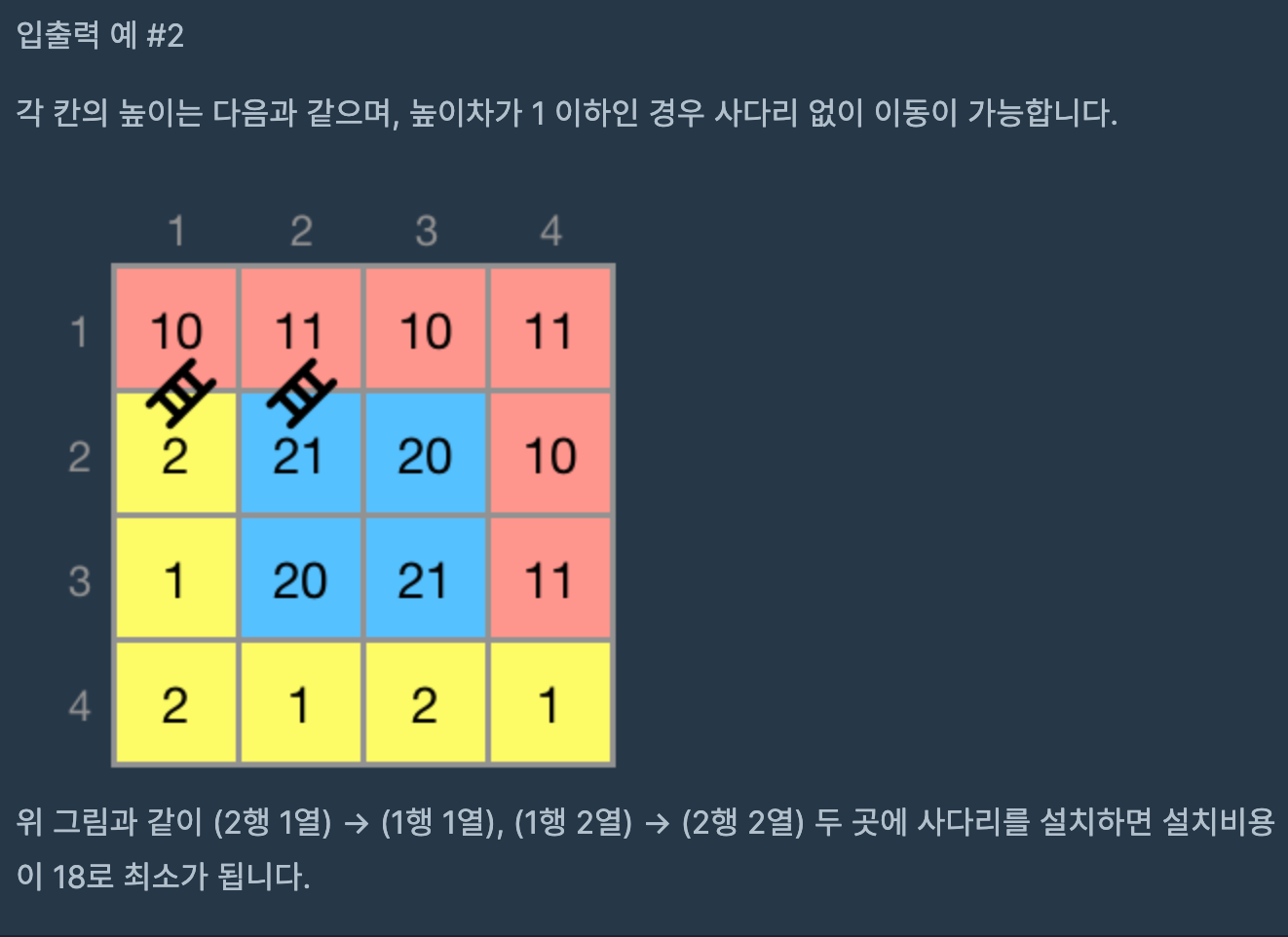
이때까지 배운 알고리즘들을 정리하기 딱 좋은 문제. 난이도가 4인 이유는 아마 구현해야할 양이 많아서 인듯 하다.
1. BFS or DFS 로 그룹 나누기
만약 height 가 3일 때 land가 아래와 같다면
land[3][3]
| 1 | 1 | 13 |
| 5 | 1 | 12 |
| 7 | 6 | 11 |
원하는 결과인
group[3][3] 는 아래와 같다. group의 각 원소는 그룹 번호를 의미한다.
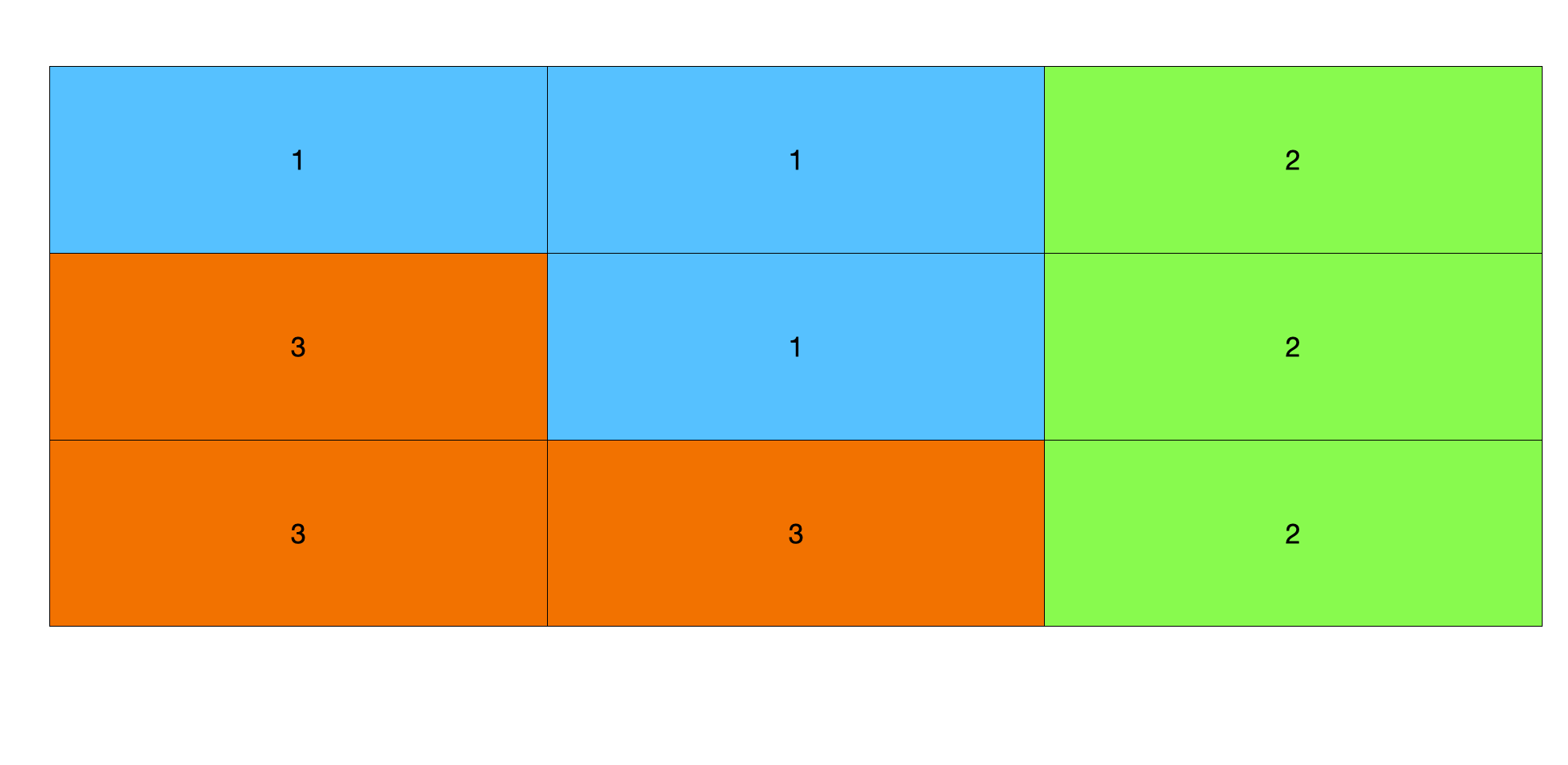
2. 인접리스트 생성하기
인접행렬로 할시 아래 처럼 메모리 초과난다.

인접 리스트의 결과물은 아래처럼 될것이다.
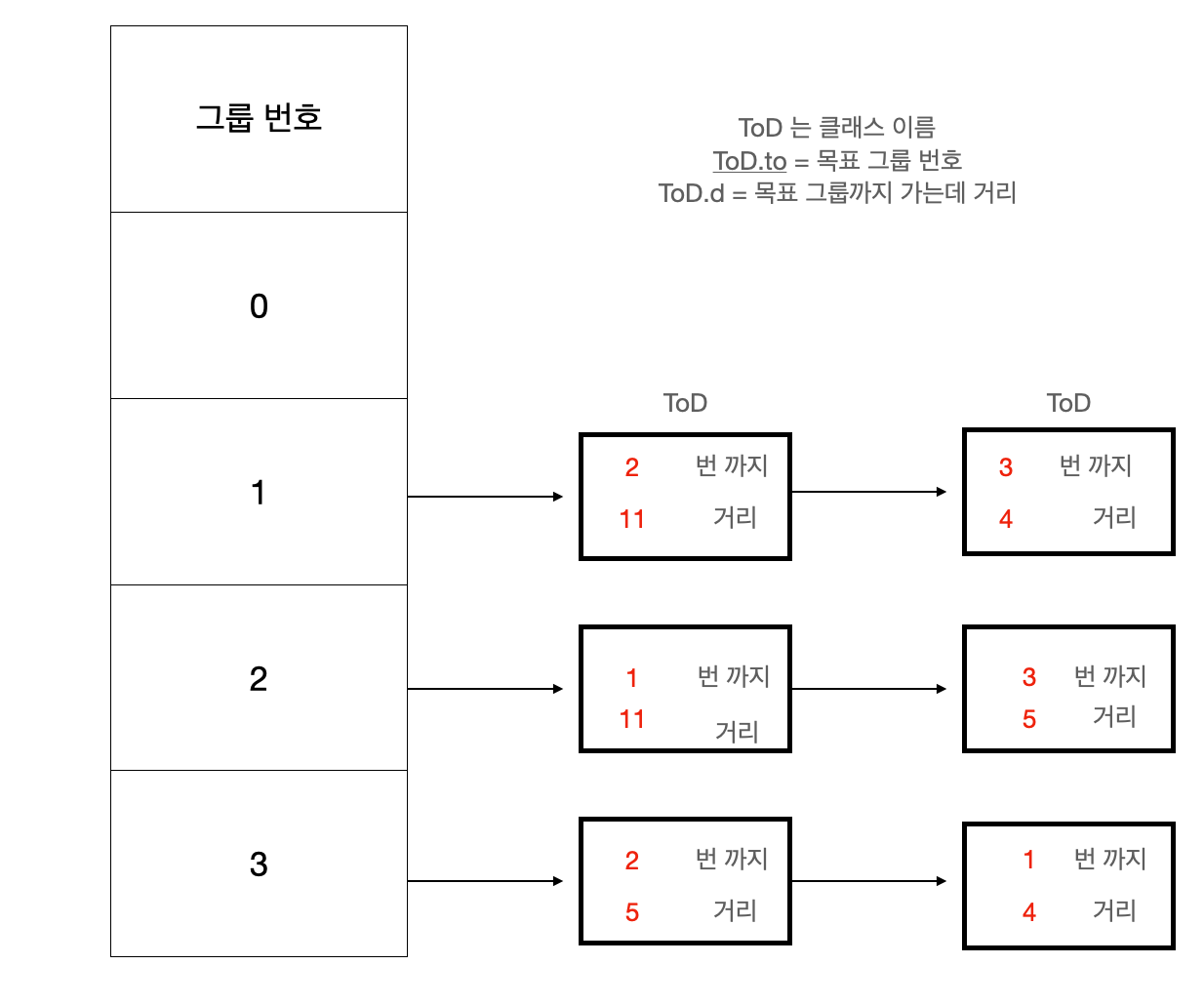
3. 거리가 작은 순으로 정렬하기
새로운 리스트와 클래스를 만들어서 정렬한다.
gn 은 다음 그룹번호다.
list 는 인접리스트를 말한다.
Node 라는 클래스 인데 Node 는 원소로 a,b,d를 가진다. 즉, 그룹번호 a와 그룹번호 b 의 거리는 d 이라는 정보를 저장하는 클래스다.
ArrayList<Node> 로 변환한뒤, 거리를 기준으로 정렬한다.
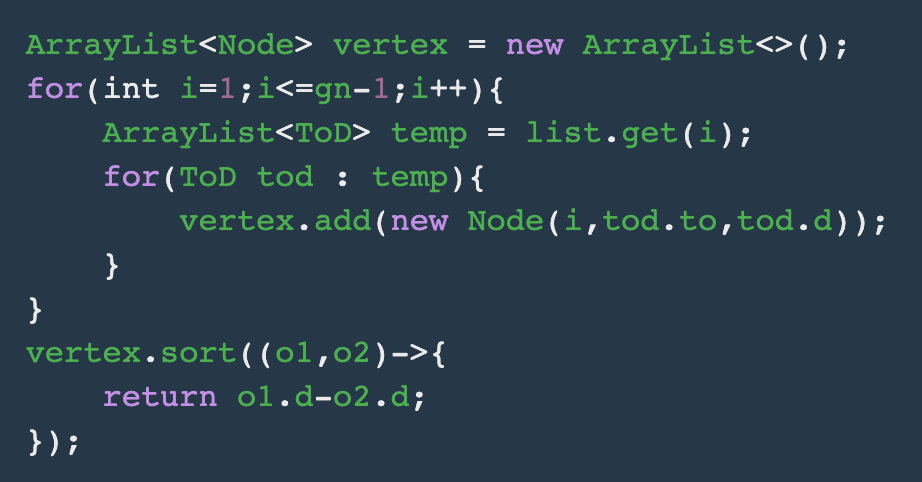
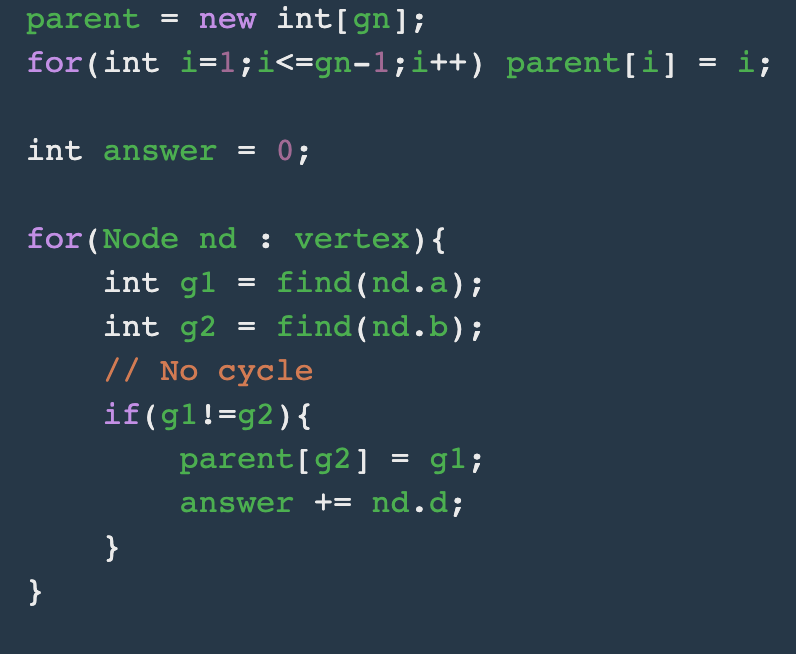
4. 크루스칼 MST 알고리즘을 적용하여 선택된 간선마다 answer에 더해준다.
<전체 코드>
import java.util.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
class Solution {
static int n;
static int[][] group;
static int gn = 1;
static int[] dx = {0,1,-1,0};
static int[] dy = {1,0,0,-1};
static int[] parent;
public int solution(int[][] land, int height) {
n = land.length;
group = new int[n][n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) group[i] = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(group[i][j]==0){
bfs(land,height,i,j);
}
}
}
ArrayList<ArrayList<ToD>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<gn;i++) list.add(new ArrayList<>());
// 간선 정보 저장
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
int x = i;
int y = j;
for(int k=0;k<2;k++){
int nx = x + dx[k];
int ny = y + dy[k];
if(rangeCheck(nx,ny) && group[nx][ny]!=group[x][y]){
int g1 = group[x][y];
int g2 = group[nx][ny];
int distance = Math.abs(land[nx][ny]-land[x][y]);
ArrayList<ToD> temp = list.get(g1);
boolean ok = false;
for(ToD tod : temp){
if(tod.to == g2){
if(tod.d > distance){
tod.d = distance;
}
ok = true;
}
}
if(!ok) {temp.add(new ToD(g2,distance));}
}
}
}
}
ArrayList<Node> vertex = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1;i<=gn-1;i++){
ArrayList<ToD> temp = list.get(i);
for(ToD tod : temp){
vertex.add(new Node(i,tod.to,tod.d));
}
}
vertex.sort((o1,o2)->{
return o1.d-o2.d;
});
parent = new int[gn];
for(int i=1;i<=gn-1;i++) parent[i] = i;
int answer = 0;
for(Node nd : vertex){
int g1 = find(nd.a);
int g2 = find(nd.b);
// No cycle
if(g1!=g2){
parent[g2] = g1;
answer += nd.d;
}
}
return answer;
}
static void bfs(int[][] land,int h,int x,int y){
Queue<Point> q = new LinkedList<>();
group[x][y] = gn;
q.add(new Point(x,y));
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Point p = q.poll();
int px = p.x;
int py = p.y;
int curHeight = land[px][py];
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nx = px + dx[i];
int ny = py + dy[i];
if(rangeCheck(nx,ny) && group[nx][ny]==0){
int nextHeight = land[nx][ny];
if(Math.abs(curHeight - nextHeight) <= h){
group[nx][ny] = gn;
q.add(new Point(nx,ny));
}
}
}
}
gn++;
}
static boolean rangeCheck(int x,int y){
if(x<0 || x>=n || y<0 || y>=n) return false;
else return true;
}
static int find(int g1){
if(g1 == parent[g1]) return g1;
else return parent[g1] = find(parent[g1]);
}
static class Point{
int x,y;
public Point(int x,int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static class ToD{
int to,d;
public ToD(int to,int d){
this.to = to;
this.d = d;
}
}
static class Node{
int a,b,d;
public Node(int a,int b,int d){
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.d = d;
}
}
}'algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] 백준 구슬탈출 2 - 13460 ( DFS & 구현) (0) | 2020.10.01 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 백준 최단 경로 1753 ( 다익스트라 알고리즘) (0) | 2020.09.27 |
| [JAVA] 백준 가르침 1062 (0) | 2020.09.24 |
| [JAVA] 백준 스도미노쿠 4574 (0) | 2020.09.24 |
| [JAVA] 백준 -부분 수열의 합 14225 (0) | 2020.09.22 |


댓글